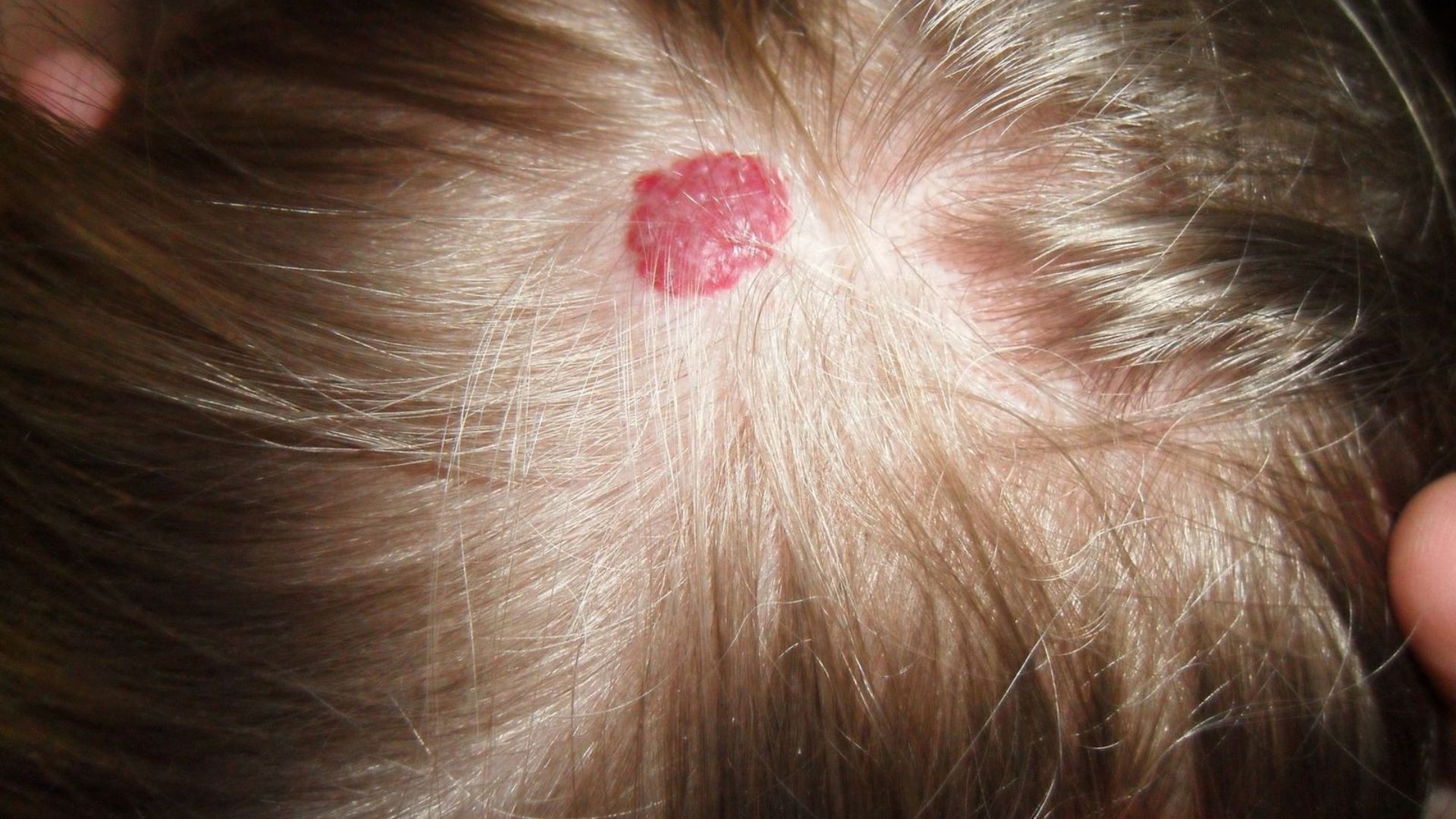
A haemangioma is a benign vascular growth caused by an abnormal collection of blood vessels. It can appear as red or purple raised lesion on the skin. It is commonly called Cherry Angioma.
Whilst harmless, some haemangiomata may grow in size, become irritated, or be removed for cosmetic (aesthetic) reasons. Bleeding is seldom reported unless the lesion is in a position to be traumatised such when shaving.
Removal is performed under local anaesthetic using a minor surgical procedure.
At Interface Clinic, no GP referral is required, and patients can self-refer for treatment but if you have seen your GP for this condition before, it is good practice to let us have the GP’s letter for your medical records with us.
Full aftercare instructions are explained and given in writing.
Scarring: Scarring is minimal with the expected outcome being some lighter coloured skin at the site of the haemangioma.
Activity Restrictions: None required but healing wound needs to be kept clean and dry for 2 days.
There is a very small chance treated haemangiomata can recur. An estimate form our practice is less than 3%. This means more than 97% will not reappear.
The local anaesthetic administration stings a bit but after that the procedure is painless.
There are specfic gene anomalies associated with haemangiomata and they happen more as we get older. They can also happen during pregnancy.
No, haemangiomas do not go away on their own.