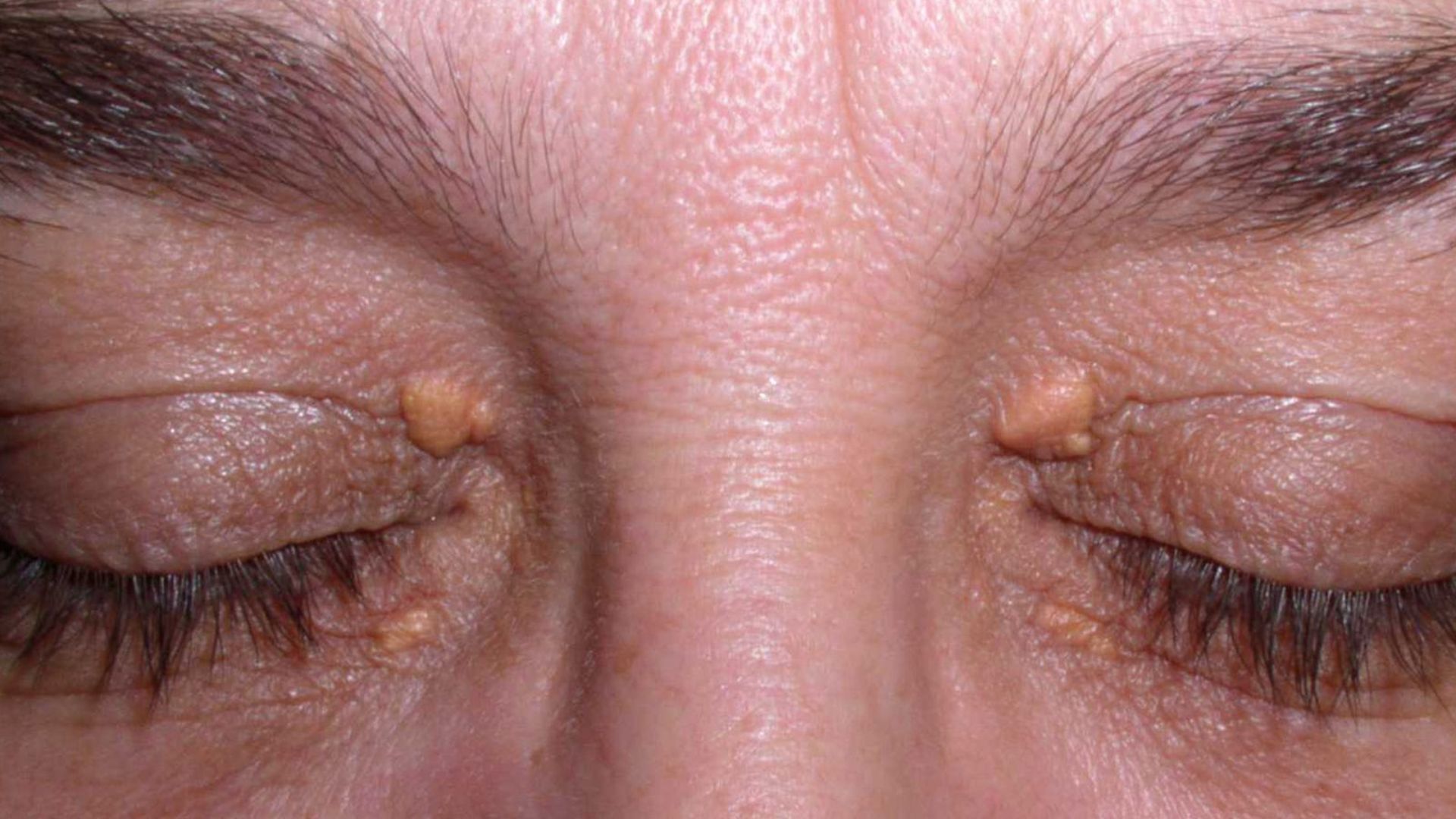
Xanthelasma is a benign yellowish cholesterol deposit that forms under the skin, typically around the eyelids. While harmless, it may gradually enlarge over time and become a cosmetic concern.
Removal is performed using minor surgical techniques under local anaesthetic.
Healing Time: The area usually heals within one to two weeks, depending on the removal method and size of the deposits.
Dressings: A dressing may be applied, and the area should be kept clean and dry.
Scarring: Some scarring may occur, but this typically fades over time, especially with proper aftercare.
Activity Restrictions: Strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days to prevent strain on the wound site.
While the removed deposits will not return, new xanthelasma can form over time, especially in individuals with high cholesterol levels.
The procedure is performed under local anaesthetic, so there is minimal discomfort. Some soreness may occur afterward.
Most wounds heal within one to two weeks, depending on the removal method and size of the deposits.